Boston, Mass. — Researchers at Mass Eye and Ear have developed a unique diagnostic tool that can detect dystonia from MRI scans, the first technology of its kind to provide an objective diagnosis of the disorder. Dystonia is a potentially disabling neurological condition that causes involuntary muscle contractions, leading to abnormal movements and postures. It is often misdiagnosed and can take people up to 10 years to get a correct diagnosis.
In a new study published September 28 in PNAS, researchers developed an AI-based deep learning platform — called DystoniaNet — to compare brain MRIs of 612 people, including 392 patients with three different forms of isolated focal dystonia and 220 healthy individuals. The platform diagnosed dystonia with 98.8 percent accuracy. During the process, the researchers identified a new microstructural neural network biological marker of dystonia. With further testing and validation, they believe DystoniaNet can be easily integrated into clinical decision-making.
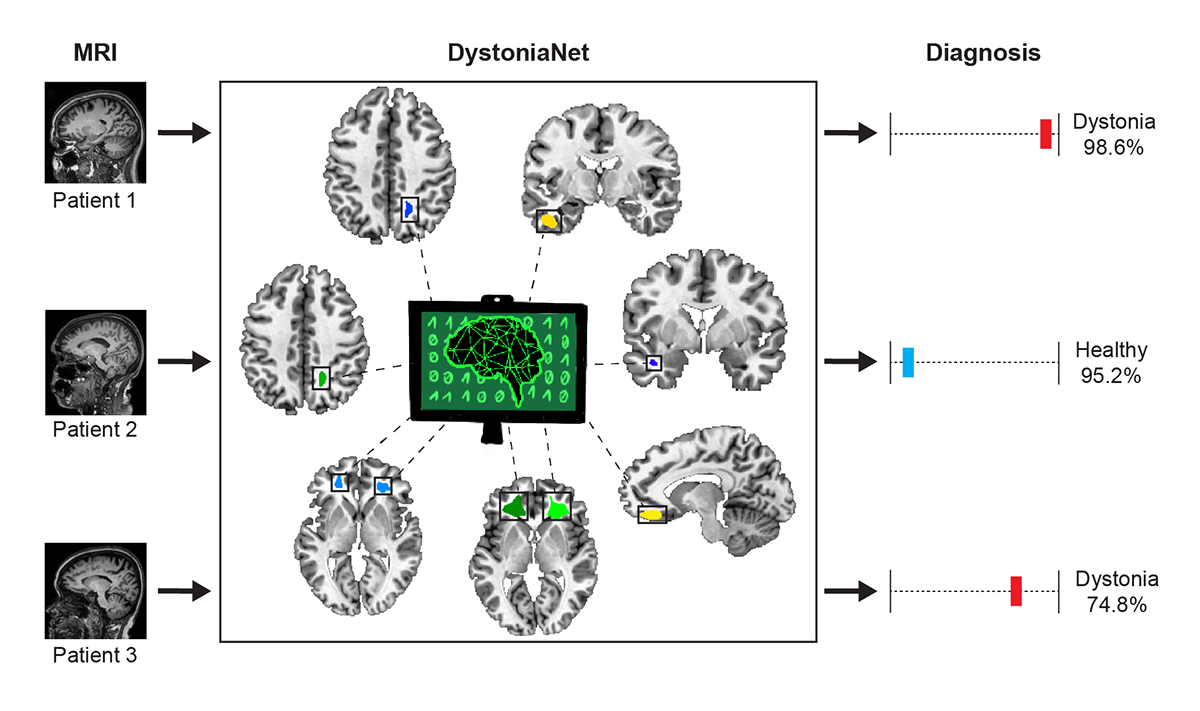
In less than one second, the AI-powered DystoniaNet platform can analyze raw MRI data to diagnose dystonia.
“There is currently no biomarker of dystonia and no ‘gold standard’ test for its diagnosis. Because of this, many patients have to undergo unnecessary procedures and see different specialists until other diseases are ruled out and the diagnosis of dystonia is established,” said senior study author
Kristina Simonyan, MD, PhD, Dr med, Director of Laryngology Research at Mass Eye and Ear, Associate Neuroscientist at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Associate Professor of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery at Harvard Medical School. “There is a critical need to develop, validate and incorporate objective testing tools for the diagnosis of this neurological condition, and our results show that DystoniaNet may fill this gap.”
A disorder notoriously difficult to diagnose
About 35 out of every 100,000 people have isolated or primary dystonia – prevalence that is likely underestimated due to the current challenges in diagnosing this disorder. In some cases, dystonia can be a result of a neurological event, such as Parkinson’s disease or a stroke. However, the majority of isolated dystonia cases have no known cause and affect a single muscle group in the body. These so-called focal dystonias can lead to disability and problems with physical and emotional quality of life.
The study included three of the most common types of focal dystonia: Laryngeal dystonia, characterized by involuntary movements of the vocal cords that can cause difficulties with speech (also called spasmodic dysphonia); Cervical dystonia, which causes the neck muscles to spasm and the neck to tilt in an unusual manner; Blepharospasm, a focal dystonia of the eyelid that causes involuntary twitching and forceful eyelid closure.
Traditionally, a dystonia diagnosis is made based on clinical observations, said Dr. Simonyan. Previous studies have found that the agreement on dystonia diagnosis between clinicians based on purely clinical assessments is as low as 34 percent and have reported that about 50 percent of the cases go misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed at a first patient visit.
DystoniaNet could be integrated into medical decision-making
DystoniaNet utilizes deep learning, a particular type of AI algorithm, to analyze data from individual MRI and identify subtler differences in brain structure. The platform is able to detect clusters of abnormal structures in several regions of the brain that are known to control processing and motor commands. These small changes cannot be seen by a naked eye in MRI, and the patterns are only evident through the platform’s ability to take 3D brain images and zoom into their microstructural details.
“Our study suggests that the implementation of the DystoniaNet platform for dystonia diagnosis would be transformative for the clinical management of this disorder,” said the first study author Davide Valeriani, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the Dystonia and Speech Motor Control Laboratory at Mass Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School. “Importantly, our platform was designed to be efficient and interpretable for clinicians, by providing the patient’s diagnosis, the confidence of the AI in that diagnosis, and information about which brain structures are abnormal.”
DystoniaNet is a patent-pending proprietary platform developed by Dr. Simonyan and Dr. Valeriani, in conjunction with Mass General Brigham Innovation. The technology interprets an MRI scan for microstructural biomarker in 0.36 seconds. DystoniaNet has been trained using Amazon Web Services computational cloud platform. The researchers believe this technology can be easily translated into the clinical setting, such as by being integrated in an electronic medical record or directly in the MRI scanner software. If DystoniaNet finds a high probability of dystonia in the MRI, a physician can use this information to help confidently confirm the diagnosis, pursue future actions, and suggest a course of treatment without a delay. Dystonia cannot be cured, but some treatments can help reduce the incidence of dystonia-related spasms.
Future studies will look at more types of dystonia and will include trials at multiple hospitals to further validate the DystoniaNet platform in a larger number of patients.
This research was funded and supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01DC011805, R01DC012545, R01NS088160), Amazon Web Services through the Machine Learning Research Award, and a charitable gift by Keith and Bobbi Richardson.
 Detecting Dystonia | New AI platform provides diagnosis with high accuracy
Detecting Dystonia | New AI platform provides diagnosis with high accuracy
 Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
 Artificial Intelligence Program Provides Rapid, Accurate Diagnosis of Dystonia
Artificial Intelligence Program Provides Rapid, Accurate Diagnosis of Dystonia
 Using an AI-Based Platform to Accurately Identify Dystonia Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by AI-Based Deep Learning Platform
Using an AI-Based Platform to Accurately Identify Dystonia Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by AI-Based Deep Learning Platform
Kristina Simonyan, MD, PhD, DrMed: Challenges in Diagnosing Dystonia (video) Davide Valeriani, PhD: Using the DystoniaNet Platform for Dystonia Diagnosis (video)
 Artificial Intelligence Is Leading the Way to Enhanced Diagnoses in Otolaryngology
Artificial Intelligence Is Leading the Way to Enhanced Diagnoses in Otolaryngology
 Amazon Research Award recipient develops new tool to diagnose dystonia
Amazon Research Award recipient develops new tool to diagnose dystonia
 New AI Platform Diagnoses Focal Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
New AI Platform Diagnoses Focal Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
 Novel AI-Based Platform Diagnoses Dystonia From MRI Scans
Novel AI-Based Platform Diagnoses Dystonia From MRI Scans
 New Artificial Intelligence Platform Uses Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
New Artificial Intelligence Platform Uses Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
 Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
 New Artificial Intelligence Platform Uses Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
New Artificial Intelligence Platform Uses Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
 Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
 Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
 Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
 Combined MRI and AI Can Identify Focal Dystonia Instantly
Combined MRI and AI Can Identify Focal Dystonia Instantly
 Detecting Dystonia in the Blink of an AI
Detecting Dystonia in the Blink of an AI
 Deep Learning AI Helps Researchers Accurately Diagnose Dystonia
Deep Learning AI Helps Researchers Accurately Diagnose Dystonia
 New artificial intelligence platform uses deep learning to diagnose dystonia with high accuracy in less than one second
New artificial intelligence platform uses deep learning to diagnose dystonia with high accuracy in less than one second
 Deep learning diagnoses disabling neurological condition on MRI in under 1 second
Deep learning diagnoses disabling neurological condition on MRI in under 1 second
 Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia in Milliseconds
Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia in Milliseconds
 Les chercheurs développent un outil de diagnostic unique pour détecter la dystonie à partir de l'IRM
Les chercheurs développent un outil de diagnostic unique pour détecter la dystonie à partir de l'IRM
 Разработан метод выявления дистонии с помощью МРТ
Разработан метод выявления дистонии с помощью МРТ
 人工智能平台可在0.36秒内高精度诊断肌张力障碍
人工智能平台可在0.36秒内高精度诊断肌张力障碍
 Дослідники розробили унікальний діагностичний інструмент для виявлення дистонії за допомогою МРТ
Дослідники розробили унікальний діагностичний інструмент для виявлення дистонії за допомогою МРТ
 Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by Artificial Intelligence-Based Deep Learning Platform
Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by Artificial Intelligence-Based Deep Learning Platform
 Una plataforma de IA diagnostica la distonía con imágenes de resonancia magnética
Una plataforma de IA diagnostica la distonía con imágenes de resonancia magnética
![]() Detecting Dystonia | New AI platform provides diagnosis with high accuracy
Detecting Dystonia | New AI platform provides diagnosis with high accuracy
![]() Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
![]() Artificial Intelligence Program Provides Rapid, Accurate Diagnosis of Dystonia
Artificial Intelligence Program Provides Rapid, Accurate Diagnosis of Dystonia
![]() Using an AI-Based Platform to Accurately Identify Dystonia Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by AI-Based Deep Learning Platform
Using an AI-Based Platform to Accurately Identify Dystonia Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by AI-Based Deep Learning Platform
![]() Artificial Intelligence Is Leading the Way to Enhanced Diagnoses in Otolaryngology
Artificial Intelligence Is Leading the Way to Enhanced Diagnoses in Otolaryngology
![]() Amazon Research Award recipient develops new tool to diagnose dystonia
Amazon Research Award recipient develops new tool to diagnose dystonia
![]() New AI Platform Diagnoses Focal Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
New AI Platform Diagnoses Focal Dystonia with High Accuracy in Less Than One Second
![]() Novel AI-Based Platform Diagnoses Dystonia From MRI Scans
Novel AI-Based Platform Diagnoses Dystonia From MRI Scans
![]() Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
Artificial intelligence platform diagnoses dystonia with high accuracy in 0.36 seconds
 Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
![]() Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
![]() Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
Researchers develop unique diagnostic tool to detect dystonia from MRI scans
![]() Combined MRI and AI Can Identify Focal Dystonia Instantly
Combined MRI and AI Can Identify Focal Dystonia Instantly
![]() Detecting Dystonia in the Blink of an AI
Detecting Dystonia in the Blink of an AI
![]() Deep Learning AI Helps Researchers Accurately Diagnose Dystonia
Deep Learning AI Helps Researchers Accurately Diagnose Dystonia
![]() Deep learning diagnoses disabling neurological condition on MRI in under 1 second
Deep learning diagnoses disabling neurological condition on MRI in under 1 second
![]() Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia in Milliseconds
Deep Learning to Diagnose Dystonia in Milliseconds
 Les chercheurs développent un outil de diagnostic unique pour détecter la dystonie à partir de l'IRM
Les chercheurs développent un outil de diagnostic unique pour détecter la dystonie à partir de l'IRM
![]() Разработан метод выявления дистонии с помощью МРТ
Разработан метод выявления дистонии с помощью МРТ
![]() Дослідники розробили унікальний діагностичний інструмент для виявлення дистонії за допомогою МРТ
Дослідники розробили унікальний діагностичний інструмент для виявлення дистонії за допомогою МРТ
 Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by Artificial Intelligence-Based Deep Learning Platform
Focal Dystonia Accurately Identified by Artificial Intelligence-Based Deep Learning Platform
![]() Una plataforma de IA diagnostica la distonía con imágenes de resonancia magnética
Una plataforma de IA diagnostica la distonía con imágenes de resonancia magnética
