About
A University Laboratory
George Tsokos' Laboratory on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Research Area
Pathogenesis of Lupus
Our research has focused on the cellular and molecular pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The laboratory has opened and led the field of molecular abnormalities on immune cells in patients with SLE. Our laboratory performs biochemical, molecular biology and cellular studies of immune and kidney cells using human material and genetically engineered mice. Molecules that are identified to contribute to immune cell malfunction are further exploited by constructing normal or lupus-prone mice engineered to express or lack each molecule to confirm their significance in vivo. A number of targets have entered or are considered to enter clinical trials by pharma. More recently we conduct studies to understand how immune elements interact with kidney resident cells. I have been uncovering mechanisms whereby resident cells through specific molecular pathways determine whether, in the context of autoimmunity, inflammation and damage will occur.
Research Area
Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Our research has focused on the cellular and molecular pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We opened and led the field of molecular abnormalities on immune cells in patients with SLE. Our laboratory performs biochemical, molecular biology and cellular studies of immune and kidney cells using human material and genetically engineered mice. Molecules that are identified to contribute to immune cell malfunction are further exploited by constructing normal or lupus-prone mice engineered to express or lack each molecule to confirm their significance in vivo. A number of targets have entered or are considered to enter clinical trials by pharma. More recently we conduct studies to understand how immune elements interact with kidney resident cells. We have been uncovering mechanisms whereby resident cells through specific molecular pathways determine whether, in the context of autoimmunity, inflammation and damage will occur.
Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011 Dec 1;365(22):2110-21. Full text: 2011-tsokos-nejm.pdf
Pathogenesis of SLE
Individual Projects
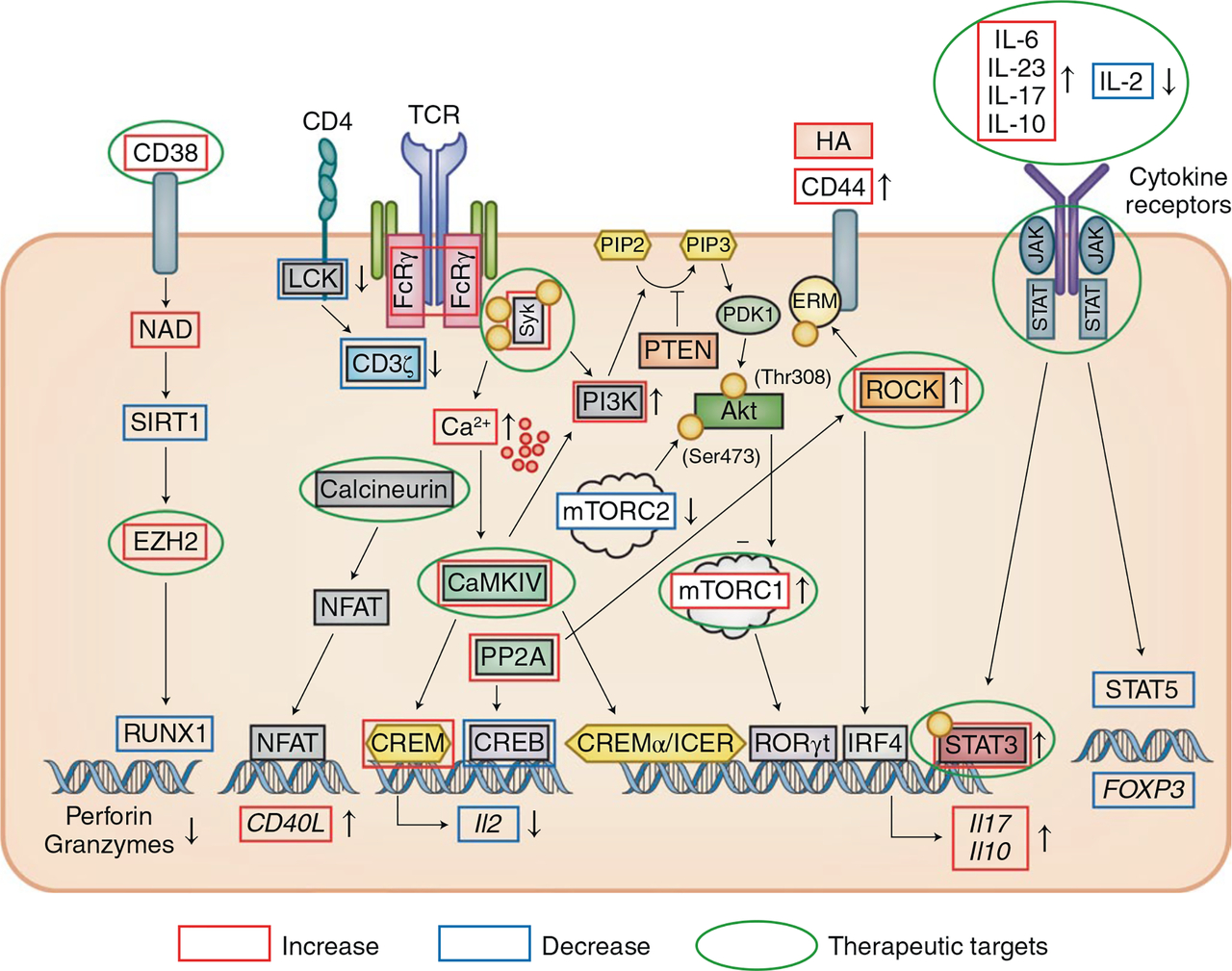
1. Aberrant early lymphocyte signaling in SLE. T lymphocytes from patients with SLE display increased and aberrant early signaling response because the T cell receptor is “rewired”.
a. Hedrich C. M., Crispin, J. C. Rauen, T., Ioannidis, C., Liossis, S. N. C., Ding, X. Z., Dennis, G. J. and Tsokos, G. C. (1998). Altered TCR/CD3-mediated protein-tyrosyl phosphorylation in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Deficient expression of T-cell receptor z chain. J. Clin Invest. 101:1448-1457.
b. Moulton, V. R., Grammatikos, A.P., Fitzgerald, L. M., Tsokos, G. C. (2013). The splicing factor SF2/ASF rescues IL-2 production in T cells from SLE patients by activating IL-2 transcription. Proc. Natl. Aca. Sci. USA. 110(5):1845-5.
c. Katsuyama, E., Suarez-Fueyo, A., Bradley, S. J., Kono, M., Kyttaris, V. C., Mizui, M., Mulki, L., Malavasi, F., Tsokos. G. C. (2020). CD38 expression in CD8 T cells compromises cytotoxic function and identifies patients with systemic lupus erythematosus prone to infections. Cell Reports. 30: 112-123.
d. Chen, P.M., Katsuyama, E., Satyam, A., Li, H., Rubio, J., Jung, S., Andrzejewski, Becherer, D., Tsokos, M. G., Abdi, R., Tsokos, G. C. (2022). CD38 reduces mitochondrial fitness and cytotoxic T cell response against viral infection in lupus patients by suppressing mitophagy. Science Adv. 2022 Jun 17;8(24):eabo4271.
-
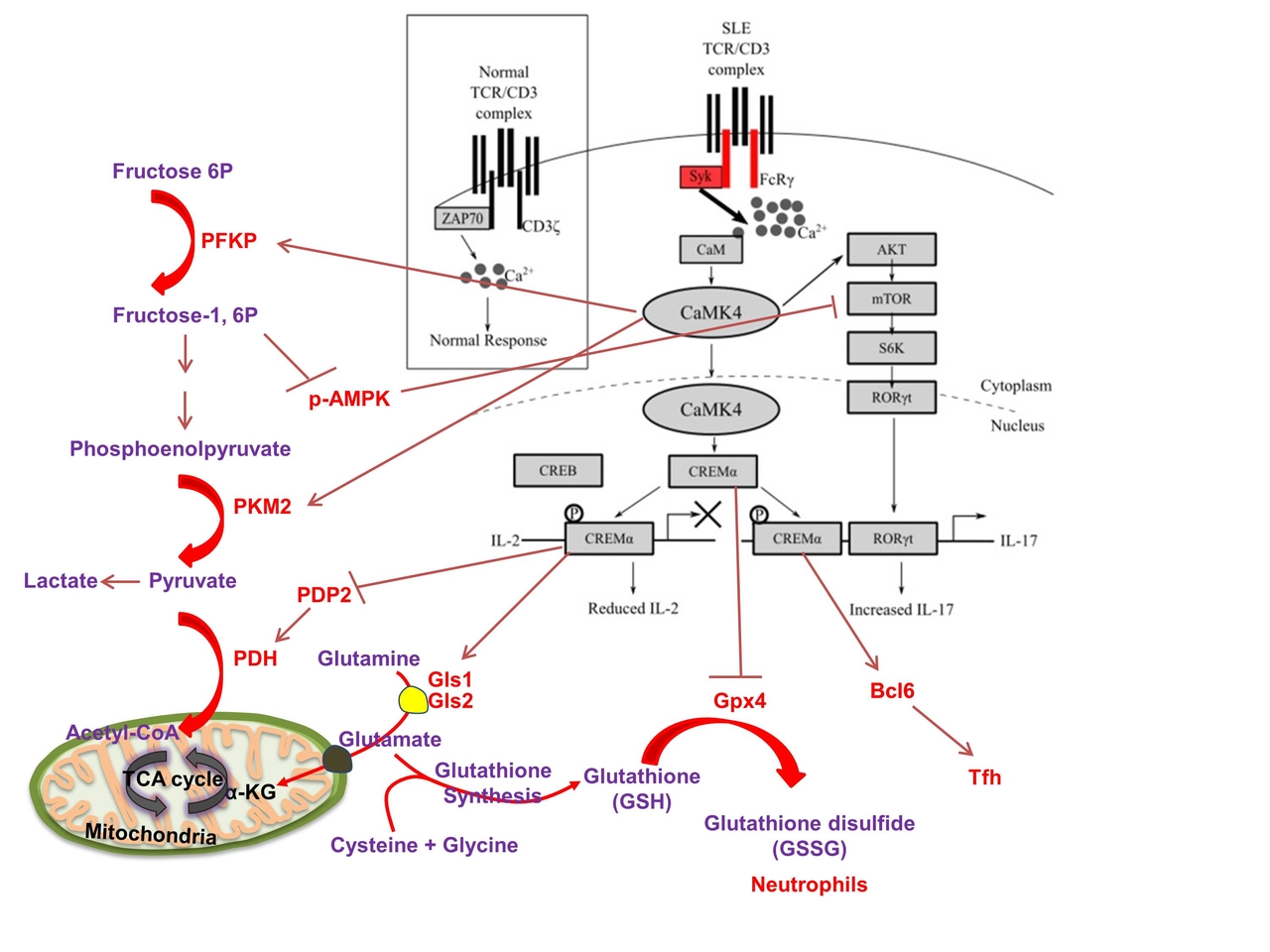
2. cAMP response element modulator alpha. A gene and function study unveils the molecular underpinnings of antithetic production of IL-2 and IL-17 in SLE.
a. Hedrich C. M., Crispin, J. C. Rauen, T., Ioannidis, C., Lo, M. S., Kyttaris, V. C., and Tsokos, G. C. (2012). cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM) a mediates CpG-DNA methylation of IL-2 and IL17A during CD4 lineage commitment and contributes to T cells subset distribution in SLE. Proc. Natl. Aca. Sci. USA. 109:16606-11.
b. Yoshida, N., Comte, D., Mizui, M., Otomo, K., Rosetti, F., Mayadas, T. N., Crispín, J. C., Bradley, S., Koga, T., Kono, M., Tenbrock, K., Karampetsou, M., Kyttaris, V. C., and Tsokos, G. C. (2016). ICER controls Th17 cell differentiation and regulates autoimmune pathology. Nature Commun. 29;7:12993. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12993.
c. Kono, M., Yoshida, N., Maeda, K., Tsokos, G. C. (2018). Transcriptional factor ICER promotes Glutaminolysis and the generation of Th17 cells. Proc. Natl. Aca. Sci. USA. 115(10):2478-2483.
d. Li, P., Jiang, M., Li, K., Xiao, X., Zhou, Y., Li, H., Xu, Y., Krisfield, S, Lipsky, P. E., Tsokos, G.C. (corresponding author), Zhang, X. (2021). Glutathione peroxidase 4 regulated neutrophil ferroptosis induces systemic autoimmunity. Nature Immunol. 22(9):1107-1117.
-
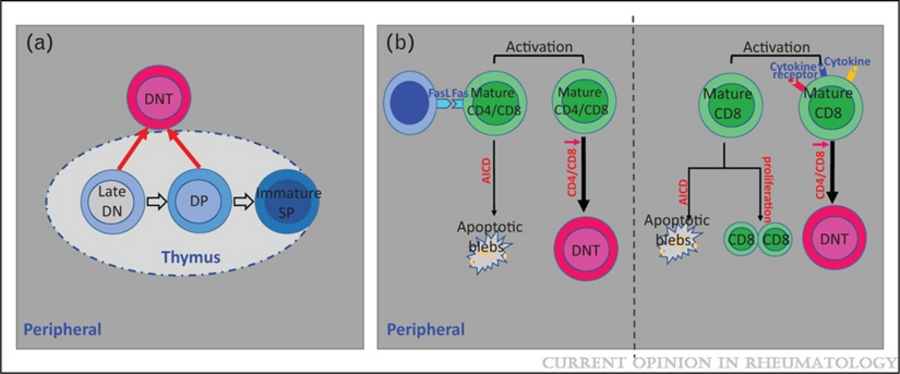
3. Double Negative (DN) Cells. CD3positive but CD4 and CD8 negative T cells are expanded in patients with SLE and provide help to B cells to produce anti-DNA antibodies and produce IL-17 and infiltrate the kidney
a. Hedrich, C. M., Crispin, J. C., Rauen, T., Ioannidis, C., Koga, T., Rodriguez Rodriguez, N., Apostolidis, S. A., Kyttaris, V. C., Tsokos, G. C. (2014). cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM)α mediates chromatin remodeling of CD8 during the generation of CD3+CD4-CD8- T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 289(4):2361-70.
b. Li, H., Tsokos, M. G., Bickerton, S., Sharabi, A., Li, Y., Moulton, V. R. Fahmy, T. M., Tsokos, G. C. Precision DNA demethylation ameliorates disease in lupus-prone mice. JCI (Insight) oi.org/101172/jci.insight.120880.
c. Li H, Adamopoulos IE, Moulton VR, Stillman IE, Herbert Z, Moon JJ, Sharabi A, Krishfield S, Tsokos MG, Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus favors the generation of IL-17 producing double negative T cells. Nature Commun. 2020 Jun 5;11(1):2859. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16636-4.
d. Li, H., Tsokos, M. G., Bhargava, R., Adamopoulos, I. E., Menn-Josephy, H., Stillman, I, E., Jordan, J., Rosenstiel, P., Tsokos, G. C. IL-23 acts renal tubular epithelial cells to drive lymphoid follicle formation in the kidney independent of IL-17. J. Clin. Invest. 2021 May 6:142428. doi: 10.1172/JCI142428
-
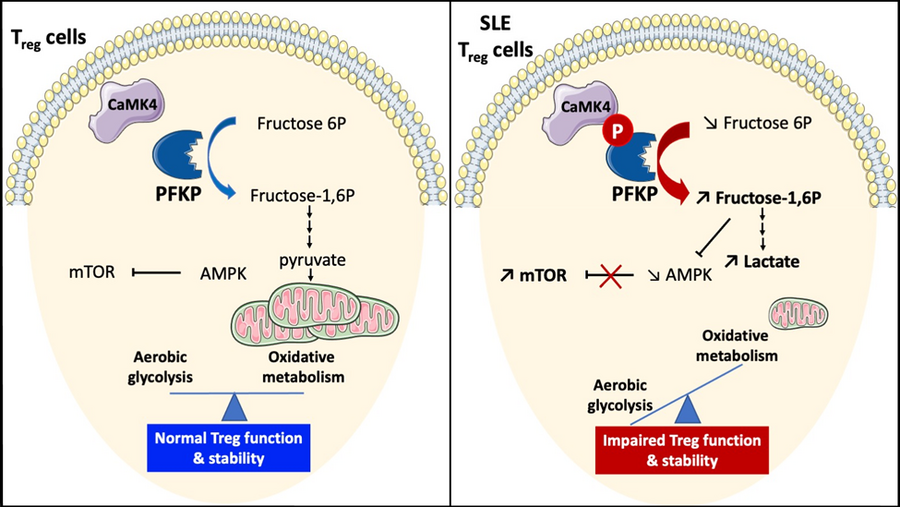
4. Calcium Calmodulin Kinase 4 in SLE. A treatment target - CaMK4 is increased in SLE T cells and tissue resident cells.
a. Juang, Y. T., Wang, Y., Solomou, E. E., Mawrin, C., Tenbrock, K., Kyttaris, V. C., and Tsokos, G. C. (2005). Systemic lupus erythematosus serum Ig increases CREM binding to the IL-2 promoter and suppress IL-2 production through CaMKIV. J. Clin. Invest. 115: 996-1005.
b. Koga, T., Hedrich, C., Mizui, M., Yoshida, N., Lieberman, L. A., Rauen, T., Crispín, J. C. Tsokos, G. C. (2014). CaMK4 promotes TH17 related autoimmune pathology though Akt/mTOR and CREM-a. J. Clin. Invest. 124(5):2234-45.
c. Maeda, K., Otomo, K., Yoshida, N., Abu-Asab, A. S., Ichinose, K., Nishino, T., Kono, M., Ferretti, A., Maruyama, S., Bickerton, S., Fahmy, T. M., Tsokos, M. G., Tsokos, G. C. 2018. Podocyte-specific delivery of calcium/calmodulin kinase inhibitor prevents autoimmune and drug-induced kidney damage. J. Clin. Invest. 128(8):3445-345.
d. Scherlinger, M., Pan, W., Hisada, R., Boulougoura, A., Yoshida, N., Vukelic, M., Umeda, M., Krishfield, S., Tsokos, M. G., Tsokos, G. C. Phosphofructokinase P fine-tunes T regulatory cell metabolism, function and stability in systemic autoimmunity. Science Adv. 8, eadc9657 (2022)
e. Scherlinger M, Li H, Pan W, Li W, Karino K, Vichos T, Boulougoura A, Yoshida N, Tsokos MG, Tsokos GC. CaMK4 controls follicular helper T cell expansion and function during normal and autoimmune T-dependent B cell responses. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):840.
-
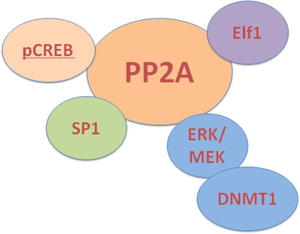
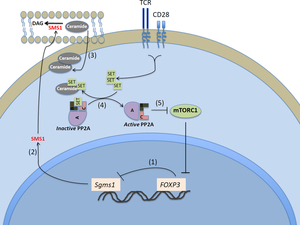
5. The first Ser/Thr Phosphatase (PP2A) in autoimmunity.
a. Katsiari, C. G., Kyttaris, V. C., Juang, Y. T. and Tsokos, G. C. (2005). Protein phosphatase 2A is a negative regulator of IL-2 production in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Invest. 115: 3193–3204.
b. Crispin, J. C. Apostolidis, S. Finnell, M. and Tsokos, G. C. (2011). Induction of PP2A Bb, a novel regulator of IL-2 deprivation-induced T cell apoptosis, is deficient in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Aca. Sci. USA.108: 12443-12448.
c. Apostolidis, S. A., Rodriguez-Rodriguez, N., Fueyo-Suarez, A., Dioufa, N., Crispin, J. C., Ezcan, E., Tsokos, M. and Tsokos, G. C. (2016). Protein phosphatase 2a is requisite for the function of regulatory T cells. Nature Immunol. 17; 556- 564.
d. Pan, W., Nagpal, K., Suarez-Fueyo, A., Ferretti, A., Tsokos, M. G., Tsokos, G. C. (2021). The regulatory subunit PPP2R2A of PP2A enhances Th1 and Th17 differentiation through activation of the GEF-H1/RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 206(8):1719-1728.
e. Pan W, Tsokos MG, Li W, Tsokos GC. (2025). Protein phosphatases in systemic autoimmunity. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2025 Feb 10;7(1):e00056. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000056.
-
6. Immunopathogenesis of lupus neprhritis.
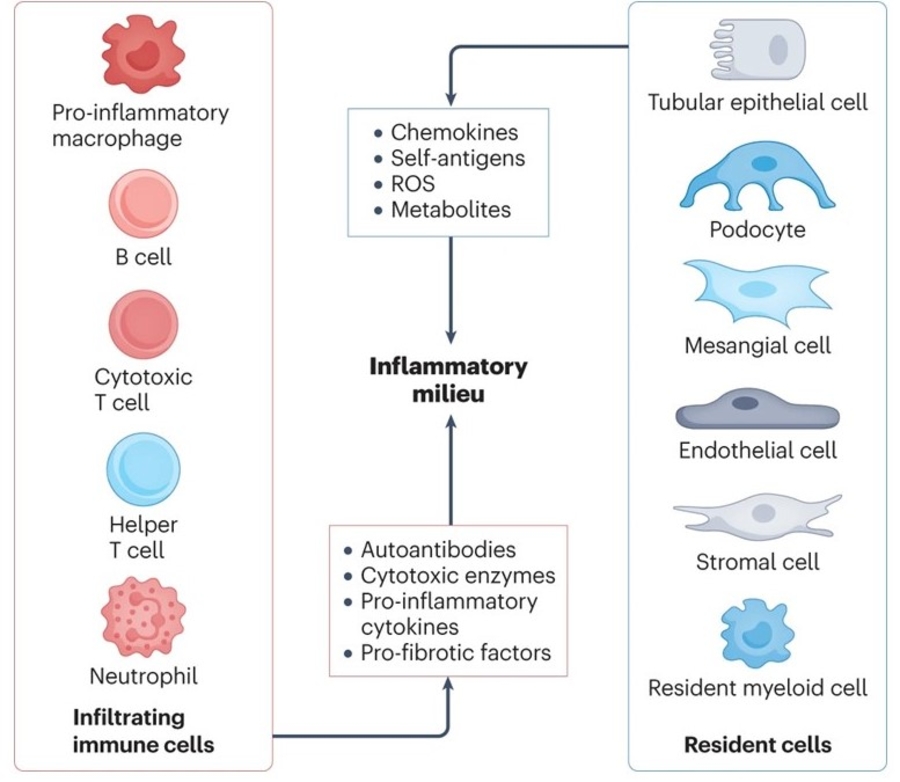
Little is known about the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis (LN), particularly as it relates to the initiation and propagation of the inflammatory response which accounts for the development or end stage renal disease. LN may complicate up to two thirds of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with higher rates commonly seen among minorities and children. Besides the needle kidney biopsy, we lack tools that reflect tissue pathology with fidelity. Although two drugs have been recently approved to treat patients with LN, all treatment protocols involve systemic administration of drugs or biologics which are laden with side effects and limited clinical efficacy. Ample evidence has revealed that kidney resident cells and newly formed high endothelial venules in the presence of an autoinflammatory environment, upregulate molecules which account for the ensuing inflammation and cell damage, while in their absence, kidney damage is averted. These molecular changes can be recorded in parallel in podocytes and tubular epithelial cells in the urine. This project will test the hypothesis that interaction of constituents of the immune system with kidney resident cells and the ectopically formed high endothelial venules, determines the development of inflammation and injury in the setting of LN: 1) Interplay between autoimmune effectors and kidney resident cells in lupus nephritis and 2) Newly formed high endothelial cells in the kidney- pathogenesis and implications in lupus nephritis.
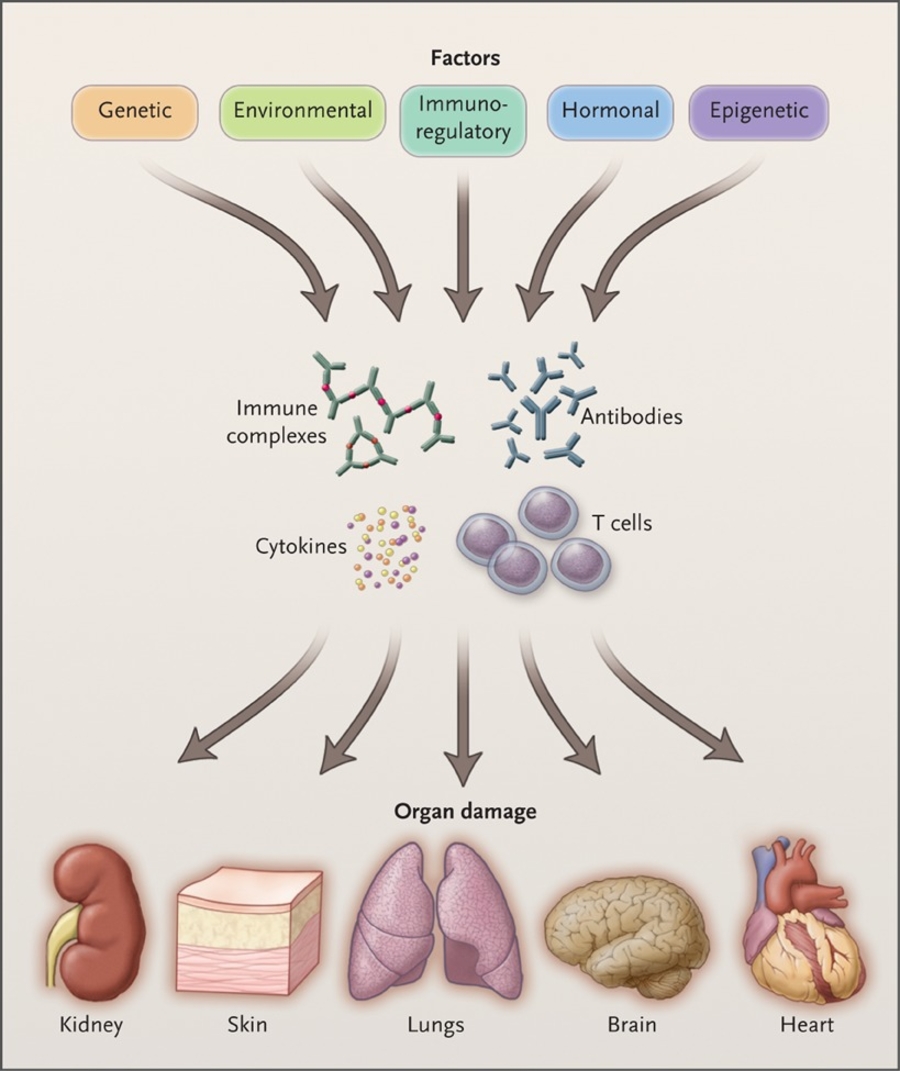
a. Tsokos, G. C. Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic autoimmunity. Nature Immunol. 21, 605-614, 2020.
b. Tsokos, G. C. Boulougoura, A., Kasinath, V., Abdi, R., Li, H. The immunoregulatory roles of non-haematopoietic cells in the kidney. Nature Rev. Nephrol. 2023 Nov 20. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00786-x.