Preeclampsia Pathogenesis and Our Drug Candidates
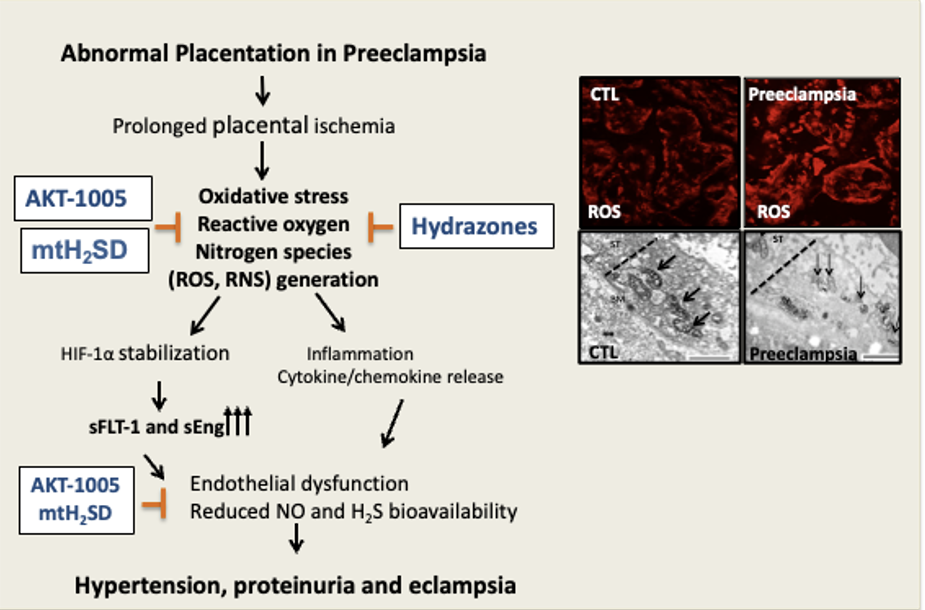
Schematic of human preeclampsia development and targeted therapies. The first stage of preeclampsia is characterized by abnormal placentation due to defective remodeling of the uterine spiral arteries, which will induce placental ischemia. We and others have proposed that this ischemic state will impair trophoblast mitochondrial function including energy production. The damaged mitochondria will release reactive oxygen species (ROS/RNS). ROS can stabilize hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1α), which will induce transcription of anti-angiogenic factors such as soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt1) and soluble endoglin (sEng) , as well as protective angiogenic factors as VEGF and placental growth factor, PlGF. The anti-angiogenic factors are released into the maternal circulation, and their actions disrupt the maternal endothelium and result in hypertension, proteinuria, and other systemic manifestations of preeclampsia. The top right inset shows increased red fluorescence, indicating the presence of ROS in the human PE placenta compared to the control (gestationally age-matched) placenta (on the left. The middle inset shows increased brown staining (nitrotyrosine) in the human PE placenta (on the right), which indicates the presence of RNS in the PE placenta compared to the control (gestationally age-matched) placenta (on the left). Bottom inset: Functional electron microscopy: Mitochondrial electron transport chain enzyme: Cytochrome C Oxidase (COX) enzyme activity is decreased in placental villous trophoblasts in preeclampsia, suggesting mitochondrial dysfunction (Right panel), compared to control placenta (on the left).
Drug groups and their benefits:
1. Organofluorine hydrazones: i, due to its high electronegativity, F atoms increase the antioxidant efficacy. ii, based on the high stability of the C-F bonds, these compounds are resistant to metabolic degradation, thus allowing lower doses. iii, the fluorine incorporation is known to increase lipophilicity and improve membrane permeability. iv, the molecules will be active in 19F NMR spectroscopy, and this selective technique can be applied for pharmacokinetic studies.
2. AKT-1005 and analogs will target both the imbalance in oxygen-centered and nitrogen-centered free radicals, and the maternal hypertension, thereby acting on multiple components underlying the pathophysiology of preeclampsia
3. Slow-release mitochondria-targeted H2S donors (mtH2SD) are 1,000 —10,000 more potent than non-targeted H2S donors. As we reported theyare capable of stimulating mitochondrial respiration and ATP synthesis, while also preventing oxidant production and mtDNA damage in an in vitro model of PE.
Therapies that specifically treat the underlying causes at an early stage of pregnancy could prevent the serious, even fatal organ dysfunction and eclampsia that characterizes preeclampsia.
