Research
How does epigenetic change contribute to tumorigenesis?
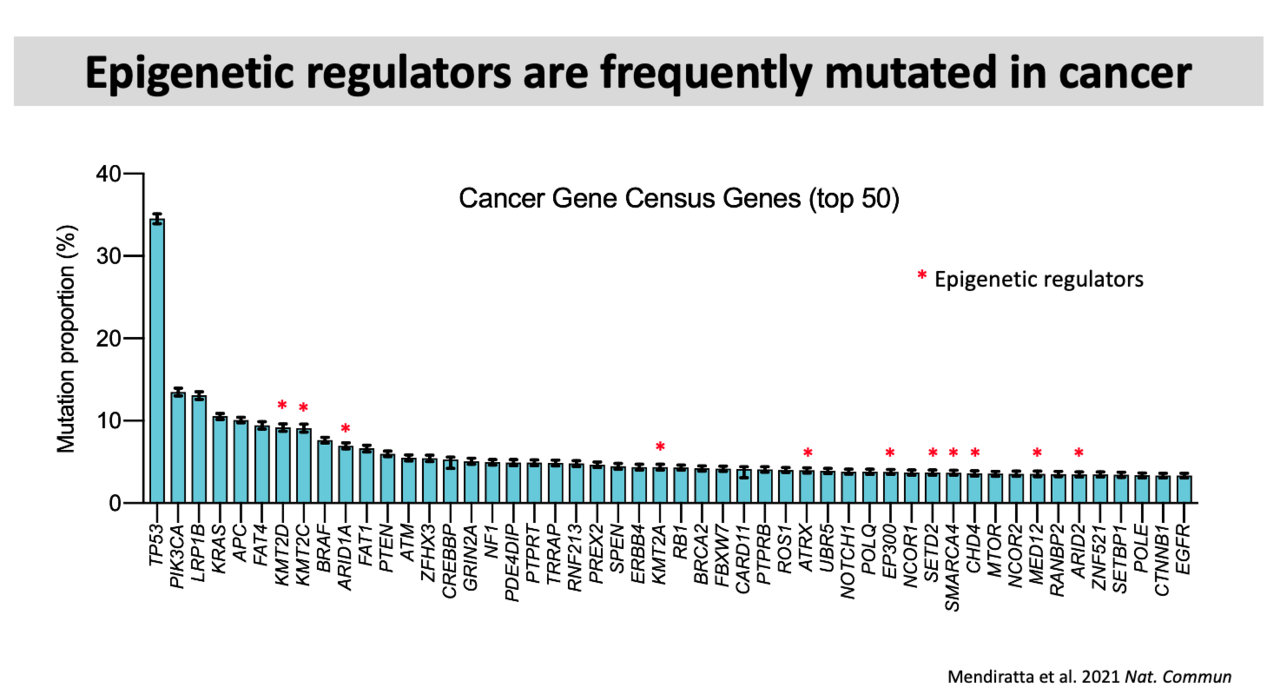
Like other tumor suppressors, epigenetic regulators often mutate in cancer (see above). However, the contribution of these mutations to cancer is not yet fully understood. Most studies have focused on epigenetic changes affecting specific genes, largely due to advances in transcriptome analysis technologies. Our lab aims to develop and implement new genomics assays to explore changes in non-coding regions, taking into account tumor heterogeneity. This approach will allow us to uncover novel mechanisms by which epigenetic alterations drive tumorigenesis.
What epigenetic vulnerability can we target to develop novel therapy?
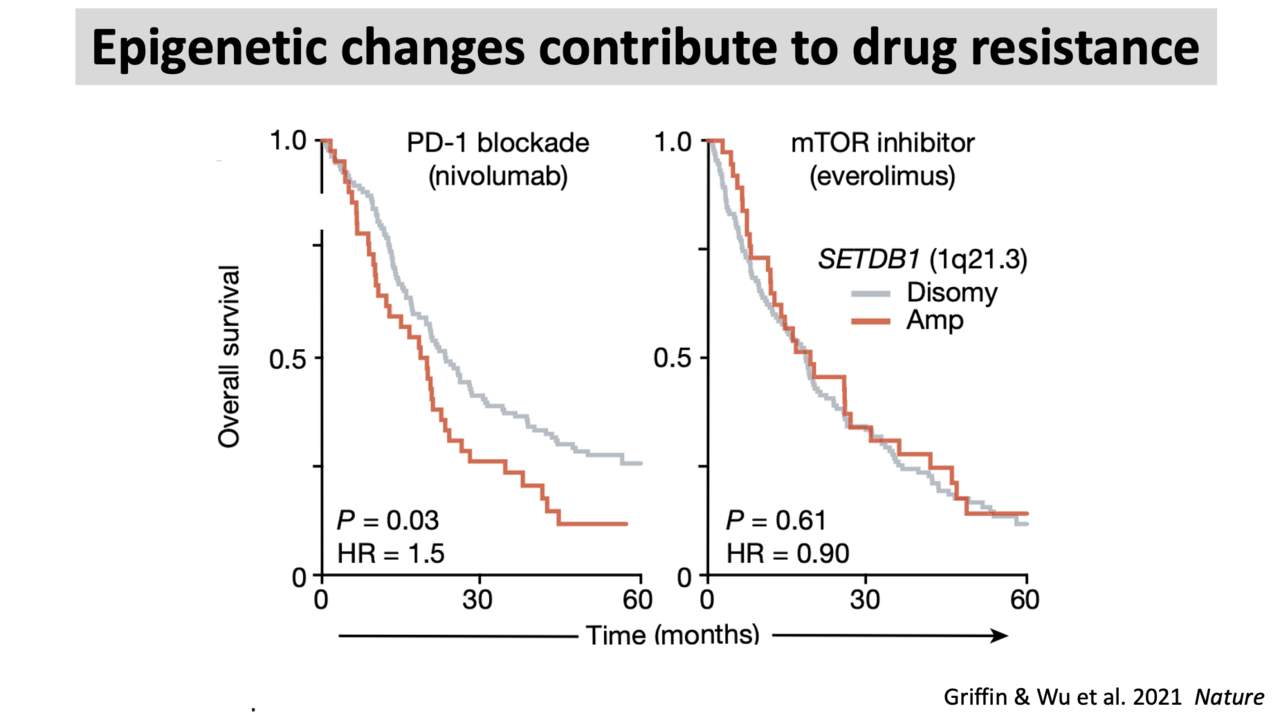
Epigenetic changes not only promote tumor development but also create vulnerabilities that make certain cancers more responsive to specific treatments or confer drug resistance. Our clinical trial data show that patients with particular epigenetic mutations respond better or worse to some therapies, but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We aim to uncover these mechanisms using both conventional and emerging epigenomic assays, with the goal of identifying biomarkers that can guide treatment selection and predict patient outcomes.
How do epigenetic drugs work?
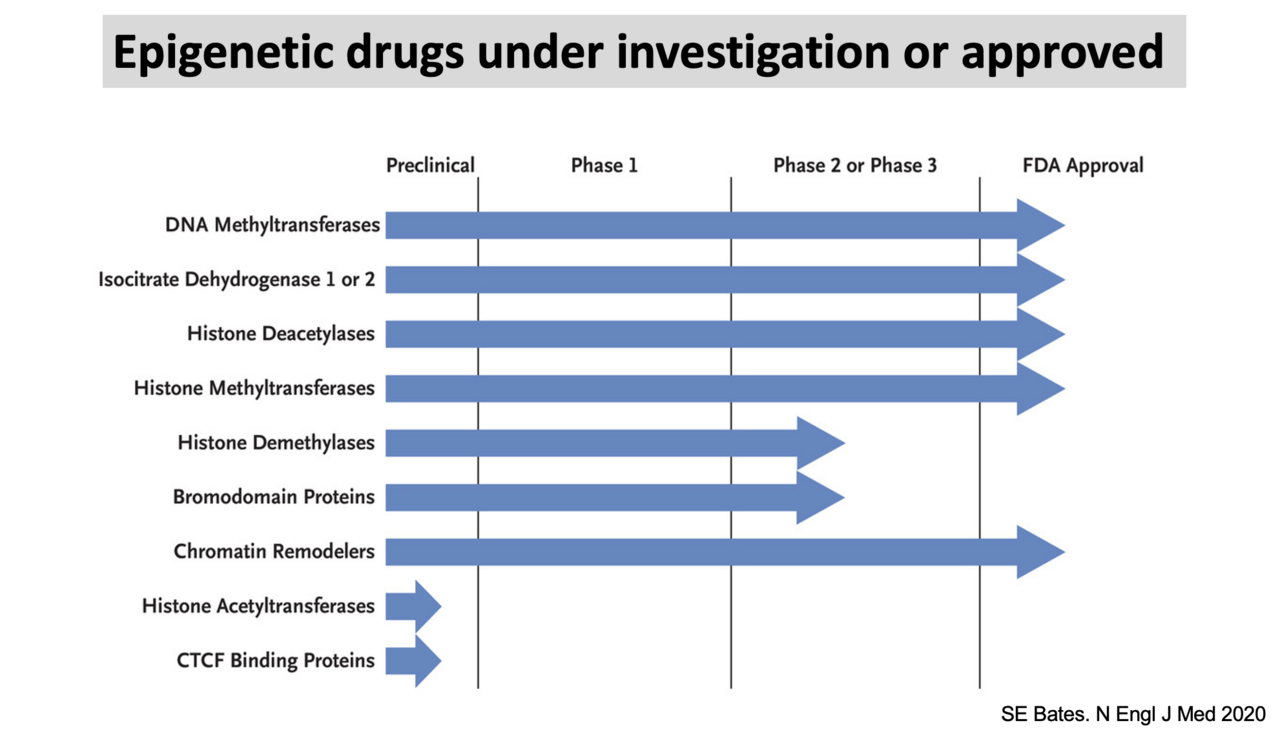
Many epigenetic drugs are currently in clinical trials or have been approved by the FDA for cancer treatment (see above). However, their effectiveness varies significantly depending on the cancer type. To maximize their potential, it’s crucial to understand how these drugs work and identify which patients are most likely to benefit. To tackle this challenge, our lab will utilize the CRISPR screening system and Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia platform at Broad Institute to identify the pathways through which these epigenetic drugs exert their effects.