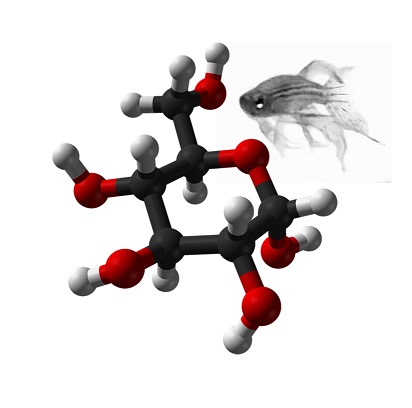
The discovery of metabolite-phenotype associations may highlight candidate biomarkers and metabolic pathways altered in disease states. We sought to identify novel metabolites associated with obesity and one of its major complications, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. In 997 individuals in Framingham Heart Study Generation 3 (FHS Gen 3), we identified an association between anandamide (AEA) and BMI. Further examination revealed that AEA was associated with radiographic hepatic steatosis. In a histologically defined NAFLD cohort, AEA was associated with NAFLD severity, the presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and fibrosis. These data highlight AEA as a marker linking cardiometabolic disease and NAFLD severity.
Publications
2017
Cisplatin holds an illustrious position in the history of chemistry most notably for its role in the virtual cure of testicular cancer. Here we describe a role for this small molecule in cyanide detoxification in vivo. Cyanide kills organisms as diverse as insects, fish, and humans within seconds to hours. Current antidotes exhibit limited efficacy and are not amenable to mass distribution requiring the development of new classes of antidotes. The binding affinity of the cyanide anion for the positively charged metal platinum is known to create an extremely stable complex in vitro. We therefore screened a panel of diverse cisplatin analogs and identified compounds that conferred protection from cyanide poisoning in zebrafish, mice, and rabbits. Cumulatively, this discovery pipeline begins to establish the characteristics of platinum ligands that influence their solubility, toxicity, and efficacy, and provides proof of concept that platinum-based complexes are effective antidotes for cyanide poisoning.
2015
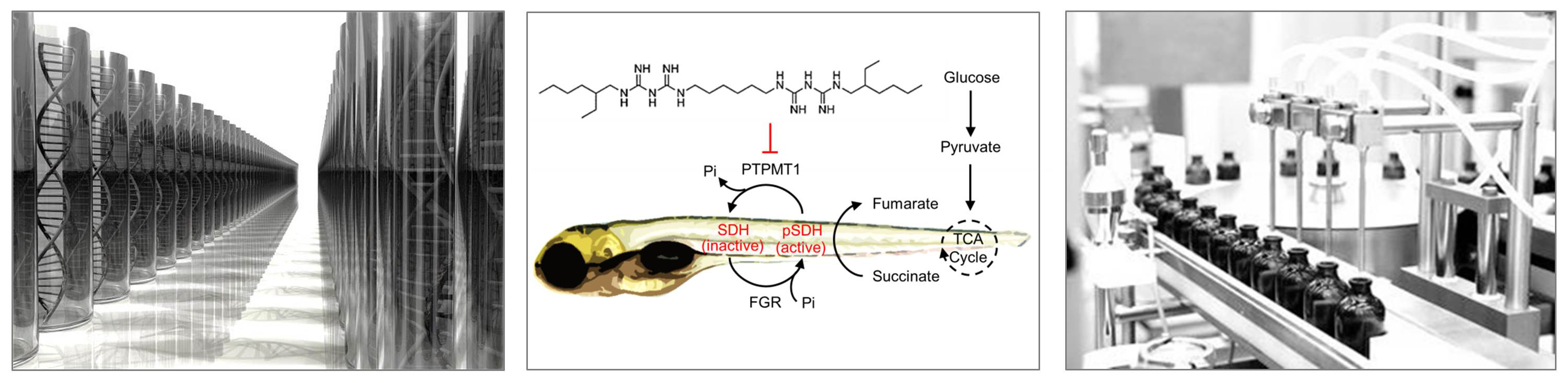
Virtually all organisms seek to maximize fitness by matching fuel availability with energy expenditure. In vertebrates, glucose homeostasis is central to this process, with glucose levels finely tuned to match changing energy requirements. To discover new pathways regulating glucose levels in vivo, we performed a large-scale chemical screen in live zebrafish and identified the small molecule alexidine as a potent glucose-lowering agent. We found that alexidine inhibits the PTEN-like mitochondrial phosphatase PTPMT1 and that other pharmacological and genetic means of inactivating PTPMT1 also decrease glucose levels in zebrafish. Mutation of ptpmt1 eliminates the effect of alexidine, further confirming it as the glucose-lowering target of alexidine. We then identified succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) as a substrate of PTPMT1. Inactivation of PTPMT1 causes hyperphosphorylation and activation of SDH, providing a possible mechanism by which PTPMT1 coordinates glucose homeostasis. Therefore, PTPMT1 appears to be an important regulator of SDH phosphorylation status and glucose concentration.
2013
Exposure to cyanide causes a spectrum of cardiac, neurological, and metabolic dysfunctions that can be fatal. Improved cyanide antidotes are needed, but the ideal biological pathways to target are not known. To understand better the metabolic effects of cyanide and to discover novel cyanide antidotes, we developed a zebrafish model of cyanide exposure and scaled it for high-throughput chemical screening. In a screen of 3120 small molecules, we discovered 4 novel antidotes that block cyanide toxicity. The most potent antidote was riboflavin. Metabolomic profiling of cyanide-treated zebrafish revealed changes in bile acid and purine metabolism, most notably by an increase in inosine levels. Riboflavin normalizes many of the cyanide-induced neurological and metabolic perturbations in zebrafish. The metabolic effects of cyanide observed in zebrafish were conserved in a rabbit model of cyanide toxicity. Further, humans treated with nitroprusside, a drug that releases nitric oxide and cyanide ions, display increased circulating bile acids and inosine. In summary, riboflavin may be a novel treatment for cyanide toxicity and prophylactic measure during nitroprusside treatment, inosine may serve as a biomarker of cyanide exposure, and metabolites in the bile acid and purine metabolism pathways may shed light on the pathways critical to reversing cyanide toxicity.
2011
2009
BACKGROUND: Cardiovascular development is vital for embryonic survival and growth. Early gestation embryo loss or malformation has been linked to yolk sac vasculopathy and congenital heart defects (CHDs). However, the molecular pathways that underlie these structural defects in humans remain largely unknown hindering the development of molecular-based diagnostic tools and novel therapies. METHODOLOGY/PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: Murine embryos were exposed to high glucose, a condition known to induce cardiovascular defects in both animal models and humans. We further employed a mass spectrometry-based proteomics approach to identify proteins differentially expressed in embryos with defects from those with normal cardiovascular development. The proteins detected by mass spectrometry (WNT16, ST14, Pcsk1, Jumonji, Morca2a, TRPC5, and others) were validated by Western blotting and immunoflorescent staining of the yolk sac and heart. The proteins within the proteomic dataset clustered to adhesion/migration, differentiation, transport, and insulin signaling pathways. A functional role for several proteins (WNT16, ADAM15 and NOGO-A/B) was demonstrated in an ex vivo model of heart development. Additionally, a successful application of a cluster of protein biomarkers (WNT16, ST14 and Pcsk1) as a prenatal screen for CHDs was confirmed in a study of human amniotic fluid (AF) samples from women carrying normal fetuses and those with CHDs. CONCLUSIONS/SIGNIFICANCE: The novel finding that WNT16, ST14 and Pcsk1 protein levels increase in fetuses with CHDs suggests that these proteins may play a role in the etiology of human CHDs. The information gained through this bed-side to bench translational approach contributes to a more complete understanding of the protein pathways dysregulated during cardiovascular development and provides novel avenues for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions, beneficial to fetuses at risk for CHDs.
2008
Blood circulation is dependent on heart valves to direct blood flow through the heart and great vessels. Valve development relies on epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), a central feature of embryonic development and metastatic cancer. Abnormal EMT and remodeling contribute to the etiology of several congenital heart defects. Leptin and its receptor were detected in the mouse embryonic heart. Using an ex vivo model of cardiac EMT, the inhibition of leptin results in a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and Snail/vascular endothelial cadherin-independent decrease in EMT and migration. Our data suggest that an Akt signaling pathway underlies the observed phenotype. Furthermore, loss of leptin phenocopied the functional inhibition of alphavbeta3 integrin receptor and resulted in decreased alphavbeta3 integrin and matrix metalloprotease 2, suggesting that the leptin signaling pathway is involved in adhesion and migration processes. This study adds leptin to the repertoire of factors that mediate EMT and, for the first time, demonstrates a role for the interleukin 6 family in embryonic EMT.