About
Meet Dr. Jennifer Ho

Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School
Director of Research, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Harrison Family Endowed Chair in Cardiovascular Research
Advanced Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Dr. Ho is an Associate Professor at Harvard Medical School, Director of Research, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, faculty member of the Heart Failure section in the at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Affiliate Member of the Broad Institute at Harvard and MIT. She completed her undergraduate studies at UC Berkeley, Harvard Medical School, followed by internal medicine residency at BWH, cardiology fellowship at UCSF, and heart failure/transplant fellowship at BWH.
She is a nationally recognized physician-scientist and her lab is focused on clinical and translational research to understand mechanisms driving HFpEF. Dr. Ho has published over 140 peer-reviewed original investigations and is the recipient of multiple NIH awards including a K24 mid-career mentoring award. Dr. Ho co-directs the CardioVascular Institute’s T32 training grant at BIDMC and serves on the Board of Directors of the Sarnoff Cardiovascular Research Foundation. She is the recipient of multiple teaching and mentoring awards including the 2023 A. Clifford Barger Excellence in Mentoring Award at Harvard Medical School.
Research Area 1
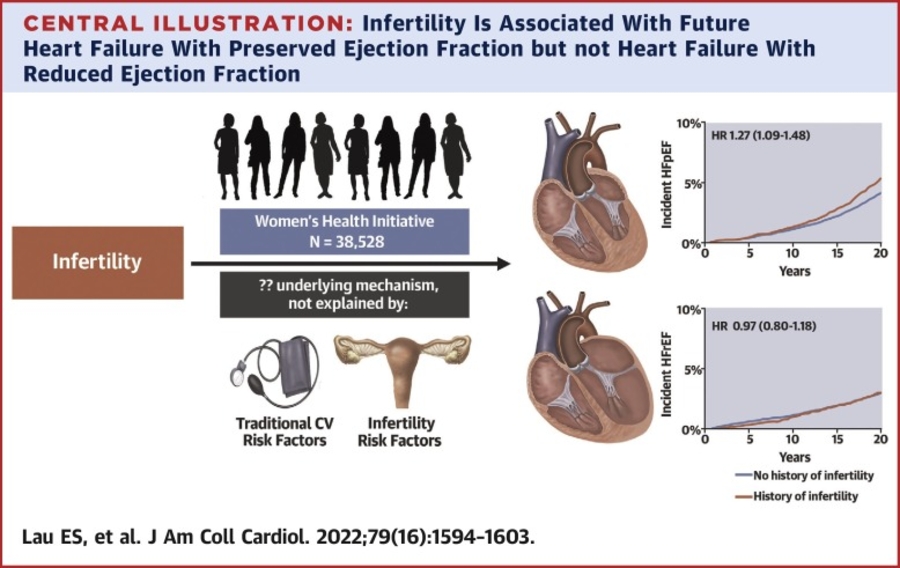
Delineating HFpEF risk and scope:
Research Area 2
HFpEF molecular mechanisms of disease:
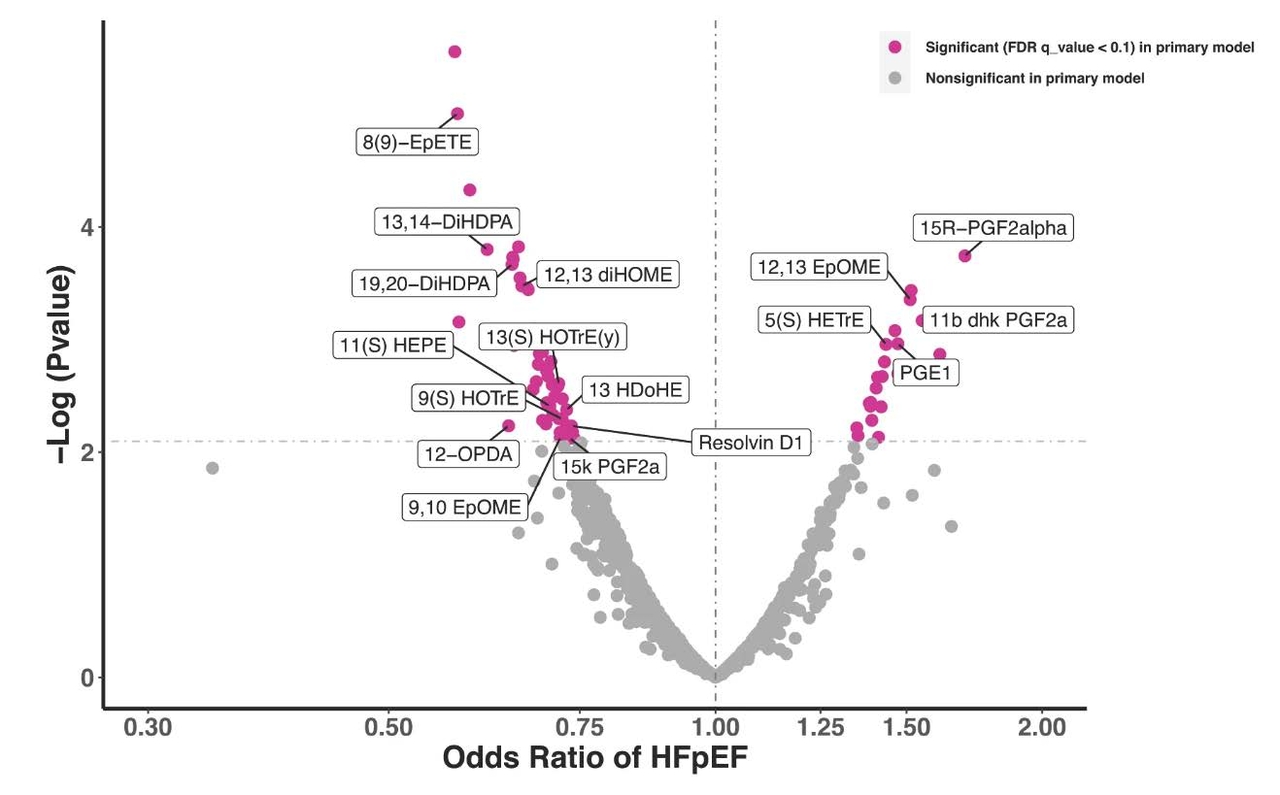
Our laboratory has leveraged molecular profiling to examine proteomic and metabolic signatures of HFpEF, work that established systemic inflammation and adiposity-related pathways as a central contributor to HFpEF development. Our group has demonstrated that eicosanoid and novel related bioactive lipids, known to govern upstream initiation of pro- and anti-inflammatory activity, are associated with HFpEF. Specifically, prostaglandin and linoleic acid derivatives are associated with greater odds, and epoxides and oxlipins with lower odds of HFpEF.
Research Area 3
Inter-organ communication in HFpEF:
An important focus of the laboratory has been to understand cardiac-vascular and cardiac-pulmonary interactions as important contributors to HFpEF pathophysiology. We previously demonstrated enhanced large artery stiffness as an important determinant of diastolic reserve. We currently are using novel approaches to isolate human venous endothelial cells to better understand the interaction between endothelial health, cardiometabolic disease, and HFpEF.