Research
Study Design
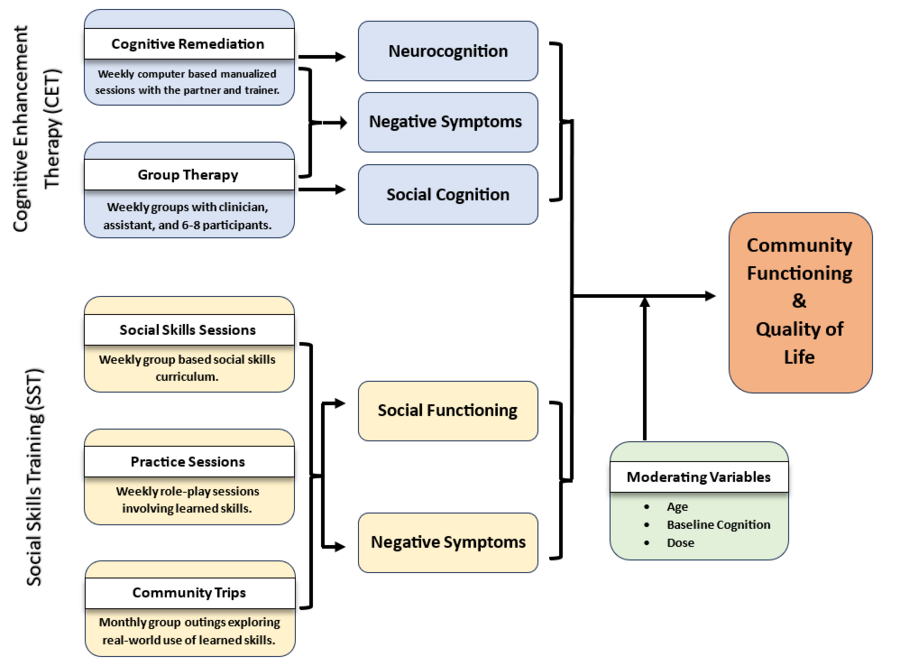
Outcomes

Community Functioning. The Social Adjustment Scale (SAS-II) distinguishes adjustment in different roles (e.g., work, school), social and leisure activities, intimate relationships, and overall adjustment. It has been validated with patient self-reports of social and community functioning.
Quality of Life. Heinrich's Quality of Life Scale is an interview-based measure with 21 questions about social functioning, role functioning, and motivation. Specific questions ask about sense of purpose, curiosity, inner drive, and related issues.
Neuropsychological Assessment. The National Institutes of Health NIH Toolbox provides measures in 6 test domains: Auditory Verbal Learning Test, List Sorting Working Memory, 9-Hole Pegboard Dexterity (motor), Pattern Comparison Processing Speed and Oral Digit Symbol Test (Speed of Processing), Flanker Inhibitory Control and Attention, Dimensional Change Card (executive functioning/reasoning & problem-solving).
Social Cognition and Skills. The Managing Emotions subscale of the Meyer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) is sensitive to treatment-related change in social cognition and social functioning in schizophrenia. Social skills are assessed with the Social Skills Performance Assessment (SSPA), a role play test that is administered by local RAs and audio-recorded, and then rated for different dimensions of social skill by blinded raters at MMHC. A short, validated version of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS-6, 6 items) is used to assess symptoms at each interview.
Qualitative Interviews
 Two randomly selected treatment participants are selected from each treatment group during month-2 of treatment delivery at each site for a qualitative interview. The interview uses an open-ended interview schedule designed to elicit information about the treatment experience and reactions to the treatment program. This process is repeated using a similar open-ended interview schedule for two randomly selected participants from each treatment group in the 11th month of their treatment.
Two randomly selected treatment participants are selected from each treatment group during month-2 of treatment delivery at each site for a qualitative interview. The interview uses an open-ended interview schedule designed to elicit information about the treatment experience and reactions to the treatment program. This process is repeated using a similar open-ended interview schedule for two randomly selected participants from each treatment group in the 11th month of their treatment.
Engagement Data
Participant Characteristics
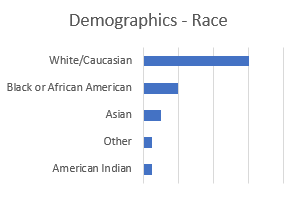 Participant characteristics assessed at baseline include age, gender, race and ethnicity, diagnosis, prior service use, family status, and living situation.
Participant characteristics assessed at baseline include age, gender, race and ethnicity, diagnosis, prior service use, family status, and living situation.
Stakeholder Engagement
 Stakeholders are people with an interest in the project. Many stakeholders are people with lived experience of serious mental illness. Some stakeholders work in mental health services.
Stakeholders are people with an interest in the project. Many stakeholders are people with lived experience of serious mental illness. Some stakeholders work in mental health services.
A project Stakeholder Committee meets quarterly each year during the project and may respond to emailed questions. Some committee members participate in a working group that reviews project findings and provides input on project articles.
Stakeholders provide feedback about project operations and suggest improvements in project procedures. Stakeholders also suggest implications of findings for programs and policies.
