Publications
2022
2021
Endothelial dysfunction accompanies the microvascular thrombosis commonly observed in severe COVID-19. Constitutively, the endothelial surface is anticoagulant, a property maintained at least in part via signaling through the Tie2 receptor. During inflammation, the Tie2 antagonist angiopoietin-2 (Angpt-2) is released from endothelial cells and inhibits Tie2, promoting a prothrombotic phenotypic shift. We sought to assess whether severe COVID-19 is associated with procoagulant endothelial dysfunction and alterations in the Tie2-angiopoietin axis. Primary human endothelial cells treated with plasma from patients with severe COVID-19 upregulated expression of thromboinflammatory genes, inhibited expression of antithrombotic genes, and promoted coagulation on the endothelial surface. Pharmacologic activation of Tie2 with the small molecule AKB-9778 reversed the prothrombotic state induced by COVID-19 plasma in primary endothelial cells. Lung autopsies from COVID-19 patients demonstrated a prothrombotic endothelial signature. Assessment of circulating endothelial markers in a cohort of 98 patients with mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19 revealed endothelial dysfunction indicative of a prothrombotic state. Angpt-2 concentrations rose with increasing disease severity and highest levels were associated with worse survival. These data highlight the disruption of Tie2-angiopoietin signaling and procoagulant changes in endothelial cells in severe COVID-19. Our findings provide rationale for current trials of Tie2-activating therapy with AKB-9778 in COVID-19.
Recent advances in proteomic technologies have made high throughput profiling of low abundance proteins in large epidemiological cohorts increasingly feasible. We investigated whether aptamer-based proteomic profiling could identify biomarkers associated with future development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) beyond known risk factors. We identified dozens of markers with highly significant associations with future T2DM across two large longitudinal cohorts (n=2,839) followed for up to 16 years. We leveraged proteomic, metabolomic, genetic and clinical data from humans to nominate one specific candidate to test for potential causal relationships in model systems. Our studies identified functional effects of aminoacylase 1 (ACY1), a top protein association with future T2DM risk, on amino acid metabolism and insulin homeostasis in vitro and in vivo. Further, a loss-of-function variant associated with circulating levels of the biomarker WAP, Kazal, immunoglobulin, Kunitz and NTR domain-containing protein 2 (WFIKKN2) was in turn associated with fasting glucose, hemoglobin A1c and HOMA-IR measurements in humans. In addition to identifying novel disease markers and potential pathways in T2DM, we provide publicly available data to be leveraged for new insights about gene function and disease pathogenesis in the context of human metabolism.
Objective: As there is significant heterogeneity in the weight loss response to pharmacotherapy, one of the most important clinical questions in obesity medicine is how to predict an individual’s response to pharmacotherapy. The present study examines patterns of weight loss among overweight and obese women who demonstrated early robust response to twice daily exenatide treatment compared to those treated with hypocaloric diet and matched placebo injections.
2020
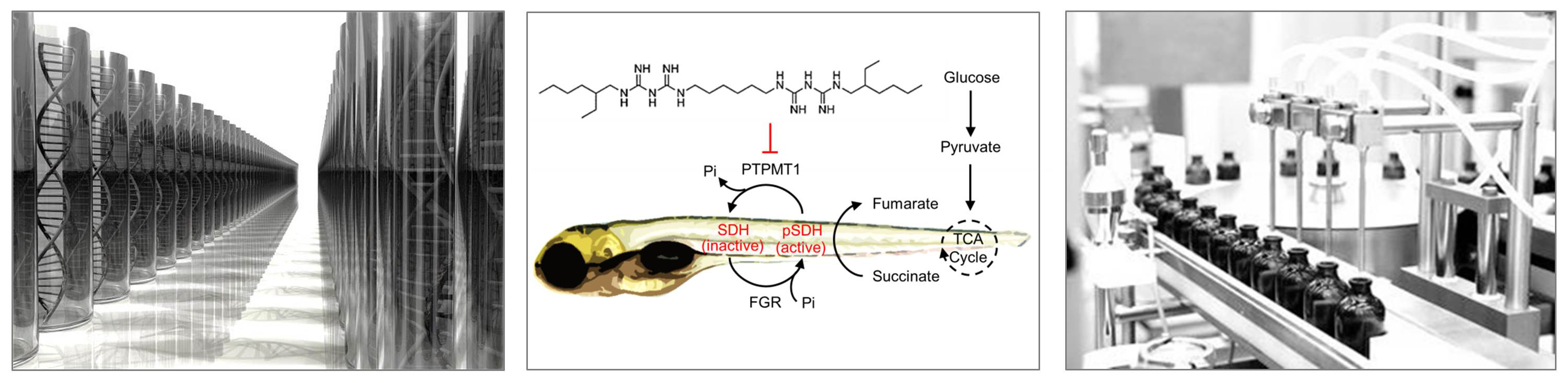
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise the largest group of membrane receptors in eukaryotic genomes and collectively they regulate nearly all cellular processes. Despite the widely recognized importance of this class of proteins, many GPCRs remain understudied. G protein-coupled receptor 27 (Gpr27) is an orphan GPCR that displays high conservation during vertebrate evolution. Although, GPR27 is known to be expressed in tissues that regulate metabolism including the pancreas, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue, its functions are poorly characterized. Therefore, to investigate the potential roles of Gpr27 in energy metabolism, we generated a whole body gpr27 knockout zebrafish line. Loss of gpr27 potentiated the elevation in glucose levels induced by pharmacological or nutritional perturbations. We next leveraged a mass spectrometry metabolite profiling platform to identify other potential metabolic functions of Gpr27. Notably, genetic deletion of gpr27 elevated medium-chain acylcarnitines, in particular C6-hexanoylcarnitine, C8-octanoylcarnitine, C9-nonanoylcarnitine, and C10-decanoylcarnitine, lipid species known to be associated with insulin resistance in humans. Concordantly, gpr27 deletion in zebrafish abrogated insulin-dependent Akt phosphorylation and glucose utilization. Finally, loss of gpr27 increased the expression of key enzymes in carnitine shuttle complex, in particular the homolog to the brain-specific isoform of CPT1C which functions as a hypothalamic energy senor. In summary, our findings shed light on the biochemical functions of Gpr27 by illuminating its role in lipid metabolism, insulin signaling, and glucose homeostasis.
2019
Cyanide is a highly toxic industrial chemical that is widely used by manufactures. Smoke inhalation during household fires is the most common source of cyanide poisoning while additional risks to civilians include industrial accidents and terrorist attacks. Despite the risks to large numbers of individuals, an antidote capable of administration at scale adequate for a mass casualty, prehospital scenario does not yet exist. Previously, we demonstrated that intravenous cisplatin analogues accelerate recovery from cyanide poisoning in mice and rabbits. Of the dozens of platinum-based organometallic complexes tested, hexachloroplatinate (HCP) emerged as a promising lead compound, exhibiting strong affinity for cyanide and efficacy across model systems. Here, we show HCP is an antidote to lethal cyanide exposure and is importantly effective when delivered intramuscularly. The pharmacokinetic profile of HCP exhibited bioavailability in the systemic circulation 2.5 minutes post-treatment and subsequent renal clearance of HCP-cyanide. HCP restored parameters of cellular physiology including cytochrome c oxidase redox state and TCA cycle metabolism. We next validated these findings in a large animal model (swine). Finally, preclinical safety studies in mice revealed minimal toxicity. Cumulatively, these findings demonstrate that HCP is a promising lead compound for development of an intramuscular injectable cyanide antidote for mass casualty scenarios.
2018
Cyanide is a potent toxic agent, and the few available antidotes are not amenable to rapid deployment in mass exposures. As a result, there are ongoing efforts to exploit different animal models to identify novel countermeasures. We have created a pipeline that combines high-throughput screening in zebrafish with subsequent validation in two mammalian small animal models as well as a porcine large animal model. We found that zebrafish embryos in the first 3 days post fertilization (dpf) are highly resistant to cyanide, becoming progressively more sensitive thereafter. Unbiased analysis of gene expression in response to several hours of ultimately lethal doses of cyanide in both 1 and 7 dpf zebrafish revealed modest changes in iron-related proteins associated with the age-dependent cyanide resistance. Metabolomics measurements demonstrated significant age-dependent differences in energy metabolism during cyanide exposure which prompted us to test modulators of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and related metabolic processes as potential antidotes. In cyanide-sensitive 7 dpf larvae, we identified several such compounds that offer significant protection against cyanide toxicity. Modulators of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, as well as the small molecule sodium glyoxylate, consistently protected against cyanide toxicity in 7 dpf zebrafish larvae. Together, our results indicate that the resistance of zebrafish embryos to cyanide toxicity during early development is related to an altered regulation of cellular metabolism, which we propose may be exploited as a potential target for the development of novel antidotes against cyanide poisoning.