microRNAs in Alcoholic Liver Disease
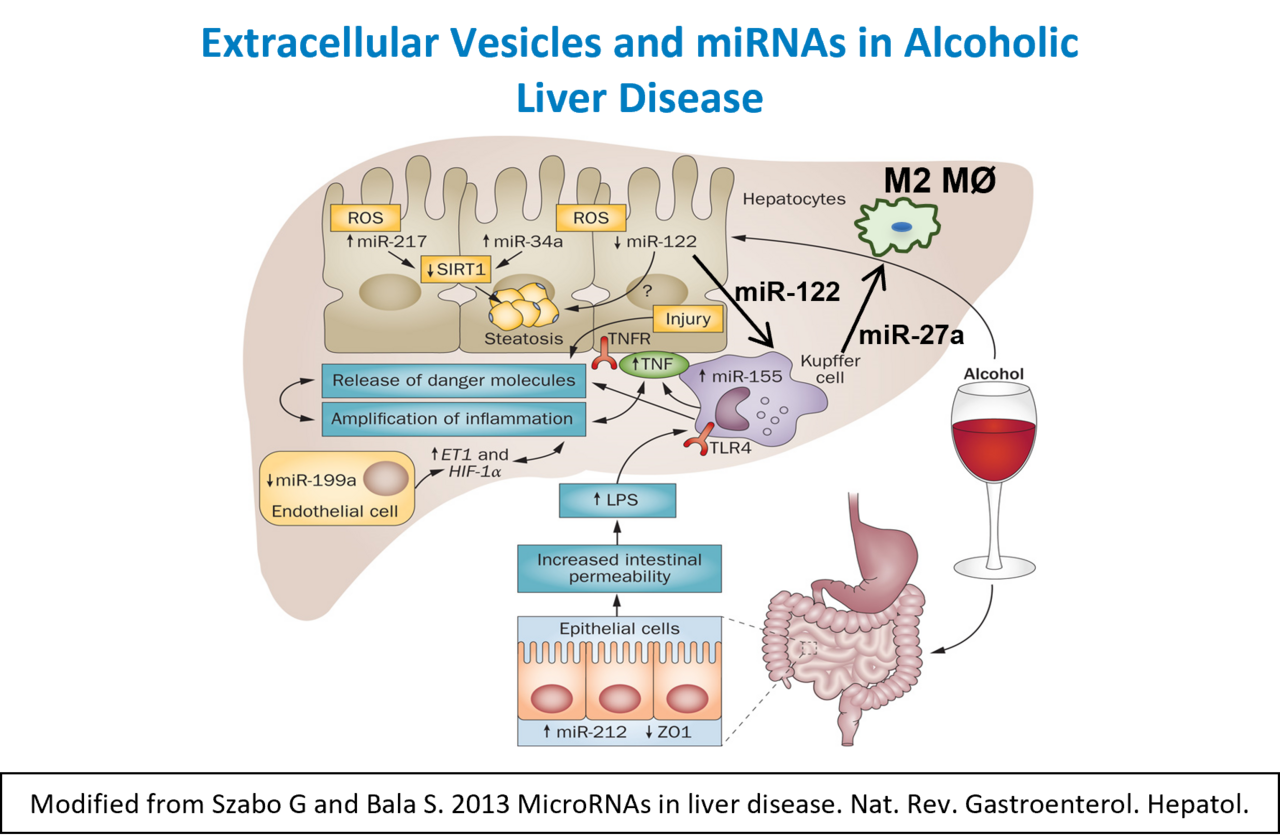
Alcoholic liver disease affects millions of people worldwide and it remains to be a therapeutic challenge for clinicians. Activation of the inflammatory cascade via gut-derived lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contributes to alcoholic liver disease via induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines induction in Kupffer cells. Micro-RNA-155 (miR-155), small non-coding RNA molecule, is important in regulation of inflammation. Our studies demonstrated that chronic alcohol up-regulates miR155 in macrophages in vitro as as as in vivo in the liver and in isolated Kupffer cells and this miR155 increase contributes to inflammation in alcoholic liver disease. We recently reported that miR-155 deficient mice are partially provoked with alcohol induced liver damage and fibrosis. Our studies on miR-155 revealed a critical role for reducing miR-155 in hepatocytes in the progression of alcoholic liver disease.
Extracellular Vesicles in Alcoholic Liver Disease: Basic and Pre-clinical Discovery
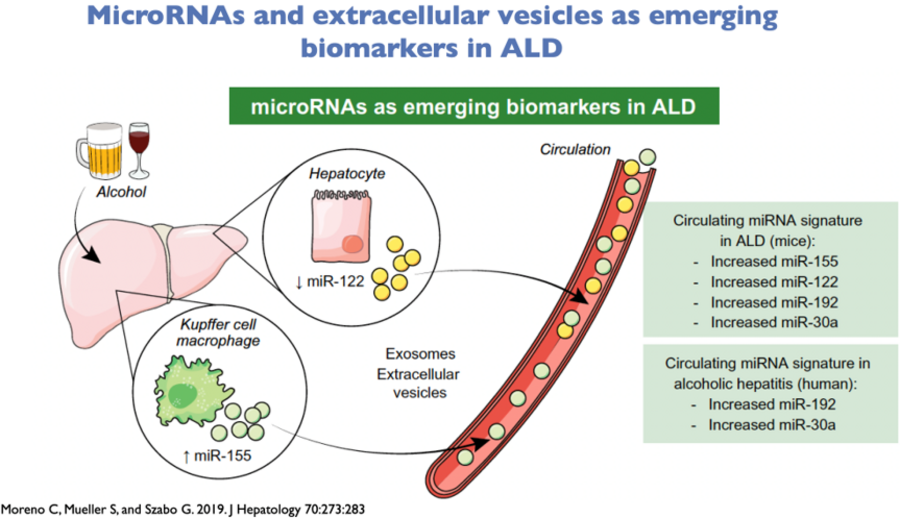
A salient feature of alcoholic liver disease is Kupffer cell activation and recruitment of inflammatory monocytes and macrophages. These key cellular events of ALD pathogenesis may be mediated by extracellular vesicles (EV). EVs transfer biomaterials, including proteins and microRNA's, and have recently emerged as important effectors of intercellular communications. Our studies indicate a specific protein signature of ALD EVs and demonstrates a functional role of circulating EVs containing heat shock protein 90 in mediating Kupffer cell and macrophage activation in the liver.
Selected Publications:
Bala S, Zhuang Y, Nagesh PT, Catalano D, Zivny A, Wang Y, Xie J, Gao G, Szabo G. Therapeutic inhibition of miR-155 attenuates liver fibrosis via STAT3 signaling. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids. 2023;33:413–427.
Babuta M, Szabo G. Extracellular vesicles in inflammation: Focus on the microRNA cargo of EVs in modulation of liver diseases. Journal of leukocyte biology. 2022;111(1):75–92.
Bala S, Babuta M, Catalano D, Saiju A, Szabo G. Alcohol Promotes Exosome Biogenesis and Release via Modulating Rabs and miR-192 Expression in Human Hepatocytes. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology. 2021;9:787356.
