Many decisions that general clinicians need to make daily are based on a risk assessment of different clinical (medical or surgical) interventions relative to the risk of non-intervention. We have a program for developing imaging protocols to better assess risk for patients in several clinical scenarios:
Pre-transplant liver and renal patients: The pre-transplant patients require coronary artery imaging to assess the risk of cardiac ischemia before major surgery such as the solid organ transplant. Unfortunately, standard coronary CTA imaging protocols yield suboptimal image quality in these patients due to their altered hemodynamic status. This results in either a suboptimal assessment of their pre-transplant risk or a need for invasive (and hence risky) imaging protocols such as coronary catheterization.
We developed two coronary CTA protocols tailored for those two distinct groups of patients:
- Pre-liver transplant patients usually have low ejection fraction, large extracellular space, and portosystemic shunting. Thus, we implemented a protocol with increased IV contrast volume and injection rate in combination with decreased kVp to increase vessel enhancement.
- Pre-renal transplant patients suffer from decreased injection fraction and severe coronary calcifications. The major change that we implemented is the application of a bone algorithm to minimize the impact of artifacts caused by coronary calcifications.
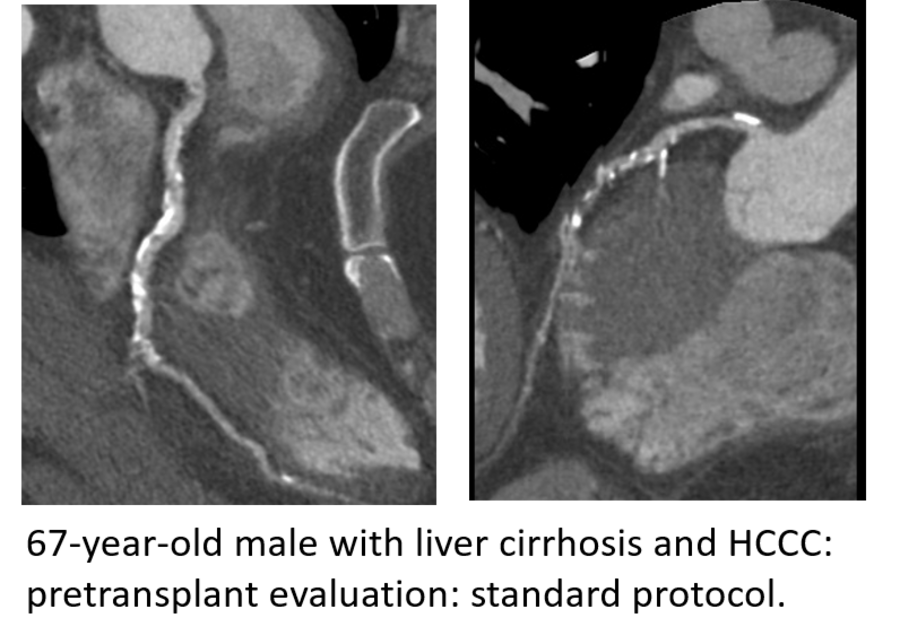
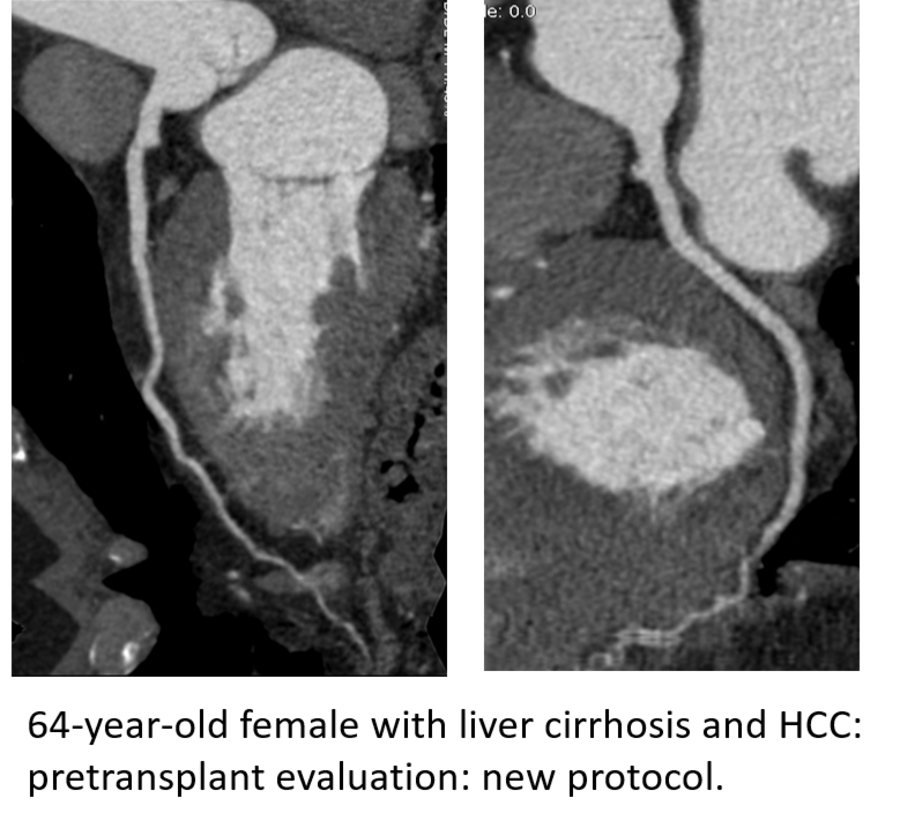
Those protocols have shown that diagnostic CCTAs can be obtained in 90% of high-risk pre-liver and kidney transplant patients and have been incorporated into standard clinical care for pre-solid organ transplant patients.
The successful implementation of this protocol led to the establishment of a new hospital-wide protocol.
