VPS35
VPS35
Vacuolar protein sorting ortholog 35 (VPS35) is a protein-coding gene and a protein complex involved in autophagy. The protein comprises a core subunit of a heteropentameric complex, known as the retromer. The retromer consists of two main components, the cargo-selective complex trimer (CSC) and the sorting nexin dimer (SNX). The retromer and its associated proteins are involved in the movement of cargo proteins from the endosomal system to the trans-Golgi network via the retrograde pathway, or back to the plasma membrane via the recycling pathway. The CSC, composed of VPS26, VPS29, and VPS35, is located in the endosomal membrane and recognizes transmembrane proteins to be sorted. VPS35 is the largest component of the CSC proteins and its function is essential for proper transport and recycling of cargo proteins[1].
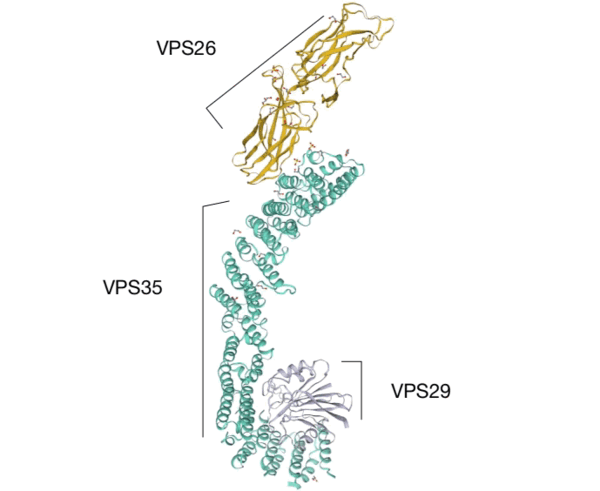
Interactive model from Swiss-Model
The endolysosomal system is implicated in the function and cell control of homeostasis, and disruptions within the system play a role in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease[2]. Evidence suggests that missense mutations in the VPS35 coding gene lead to retromer dysfunction and may contribute to late-onset autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease via the single AspD620Asn (D620N) missense mutation. Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated overexpression of D620N VPS35 in the substantia nigra result in the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons, making the D620N mutation worthy of deeper study.
1. Williams ET, Chen X, Moore DJ. VPS35, the Retromer Complex and Parkinson's Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017;7(2):219-233. doi: 10.3233/JPD-161020.
2. Williams ET, Chen X, Otero PA, Moore DJ. Understanding the contributions of VPS35 and the retromer in neurodegenerative disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2022 Aug;170:105768. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105768.
