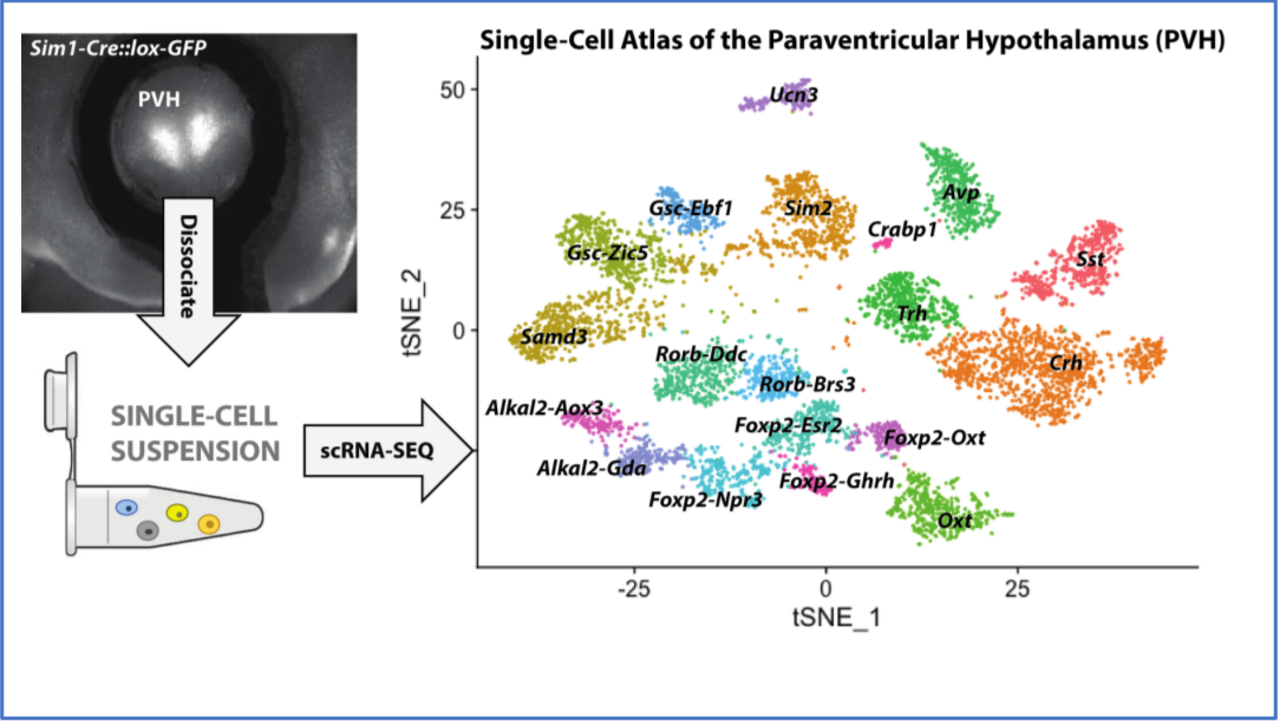
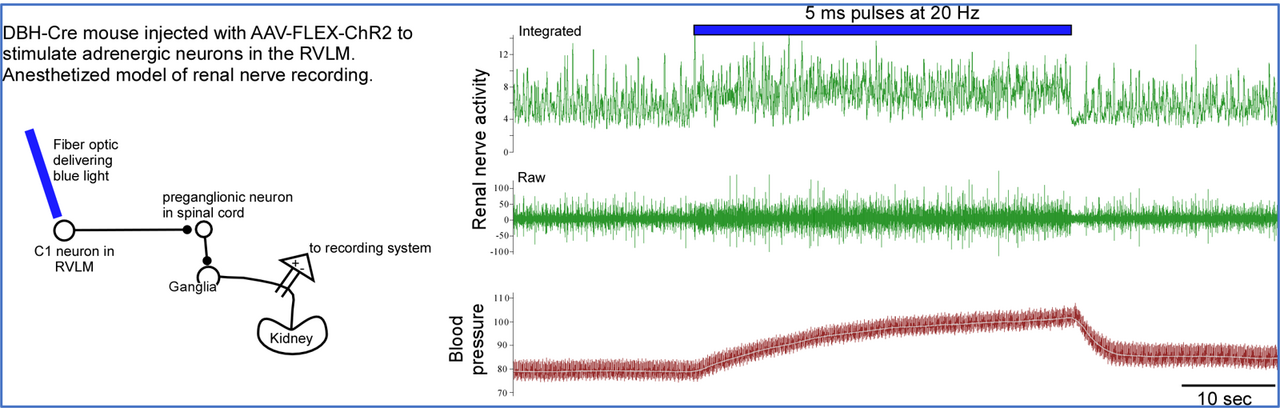
Prior work by others suggests that renal nerves arise from several neuron subpopulations in sympathetic ganglia. It is possible that these specific subpopulations of neurons, as well as the CNS circuits that innervate them selectively control tubular transport, glomerular filtration rate or renin release. This NIH funded project aims to create the tools to define the individual subpopulations of brainstem neurons which connect to the preganglionic neurons that control sympathetic postganglionic neurons important for renal function.
Neurons originating from the paraventricular hypothalamus (PVH) and other hypothalamic nuclei, the medullary raphe pallidus, as well as the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) and the A5 cell group in the pons project to the intermediolateral column (IML) at the T8 – T12 spinal cord, where nearly all renal sympathetic preganglionic fibers originate.
Combined, PVH, RVLM and A5 neurons provide the vast majority of brain input to the spinal cord, and the proposed studies will focus on neuron subpopulations in these brain areas which control kidney function.